What is grid-tied solar power?
Grid-Tied PV System, also known as “On-Grid” solar power system, is a solar power generation system that is directly connected and connected to the grid. at the connection point, the generated electric energy is mixed into the public power system and jointly supplied to the loads for use, when the electrical energy generated from the system is less than the demand of the load, a part of the energy is offset from the public grid and vice versa when the demand for electricity is less than the amount of electricity generated, the excess energy of the system will be “flowed” into the grid. In this solution, the public grid system plays the role of both providing energy, storing and regulating energy, so that the solar power system is always controlled for maximum power generation without the need for electricity. must self-regulate according to the load demand to make full use of this clean energy source, besides, there is no need to calculate and balance the power consumption of the load when designing and installing the solar power system as well. as there is no need to invest in a battery / storage battery system to “back-up” and regulate energy.
System Operation:
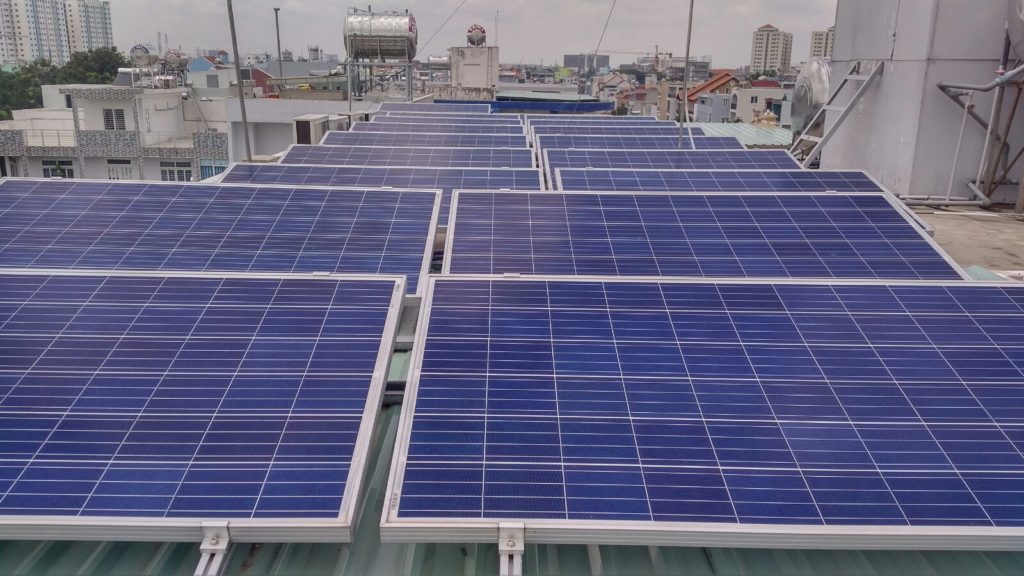
Solar panels are connected to each other in arrays and installed to best capture energy from the Sun’s radiation and convert it into electricity in the form of direct current, this current will be Inverter (Inverter) modulates into alternating current and automatically adjusts electrical parameters such as voltage, frequency, phase angle to satisfy the conditions of harmonization and connection to the grid at the connection point, this inverter is called Grid-tied solar inverter.
Benefits of the solution:
The grid-tied solar power solution solves many disadvantages for solar energy, which is an intermittent energy source and cannot control the source but only the receiving system. Utilizing the electrical system as a storage, conditioning and co-supply system for the load will allow maximum solar energy collection and bring many benefits.
-
Unlimited load, make the most of:
The system allows maximum solar energy collection and does not need to calculate the load balance when investing in the system and is not required to limit the consumption capacity of the load.
-
Flexible investment:
The capacity can be invested in accordance with the conditions of the installation area and can be divided into many investment stages in accordance with the investment ability.
-
System with high stability, long service life:
The main equipment in the system such as panels, inverters are manufactured with durability and design life of over 20 years and do not use battery/storage batteries which are low-durability devices.
-
Low investment cost:
Because there is no need to invest in a battery/battery system, this solution significantly reduces investment costs compared to a standalone system (Off-Grid).
-
Low operating and maintenance costs:
The main units are designed to be maintenance-free or low-maintenance and operate fully automatically without the need for operator along with allowing remote monitoring via PC and mobile devices, so the system has almost no operating costs.
Cons of the solution:
The grid-tied solar power solution brings many benefits, but there are also disadvantages that investors need to consider when deciding to invest.
-
Không vận hành được khi mất điện:
Because the system is connected to the public grid, when the power grid loses power, the system will automatically separate from the power system, which means that if there is a power outage to the public grid, the load will also lose power according to the surface. This is during sunny times and of course not in areas without electricity.
-
Must be licensed:
The public power system is like a “buffer” so the connection to the grid must be approved by the Electricity and the State management agency and the system must meet the standards as well as the power quality according to the regulations. determined. In Vietnam, the connection of the power system to the grid has been allowed under the Prime Minister’s Decision No. 11/2017/QD-TTg and specified in the Circular No. 16/2017/TT-BCT of the Ministry of Industry and Trade. with the active support of EVN.
-
System Limits:
The use of the public electricity system as a “buffer” system (storage and conditioning), so the total capacity of solar energy in a country or region depends on the “conditioning” capacity of the system. in that country or region. In Vietnam, according to the power plan VII, the total capacity for renewable electricity including Wind power, Solar power and Biomass power is 850MW by 2020 and expanded by 4,000MW by 2030. However, this should be done. interested in solar power generation plants with large capacity up to tens of MW.
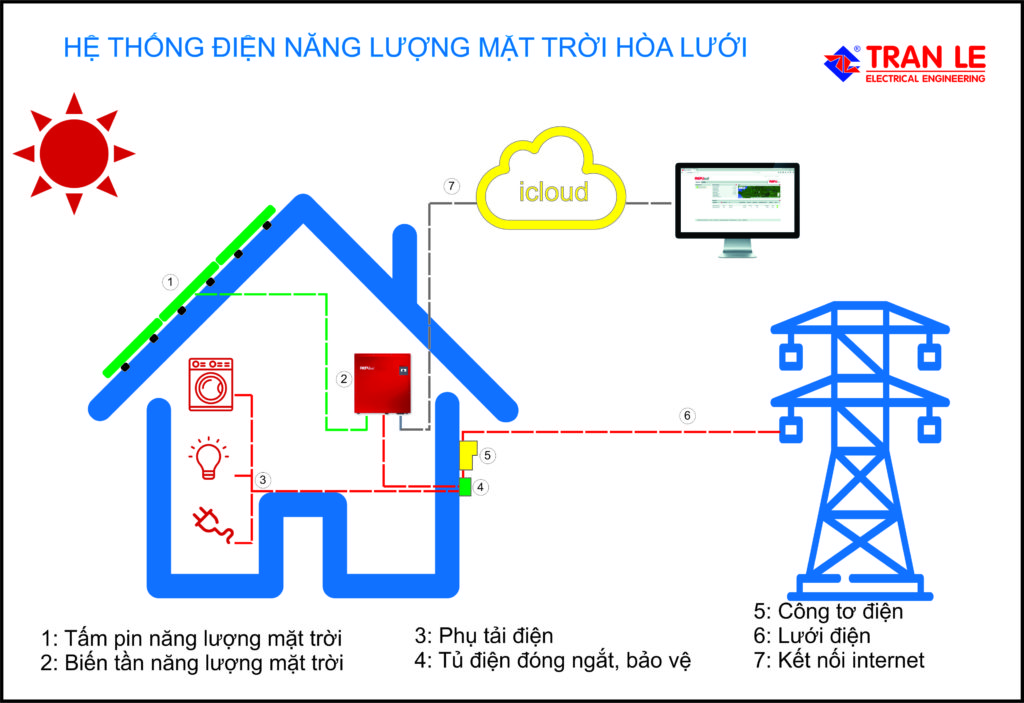
The main devices in the system:
-
Solar panels:
- Solar panels are linked into arrays, installed to absorb maximum energy from solar radiation and convert it into electricity. Solar panels account for most of the investment costs and are decisive in terms of energy conversion efficiency.
-
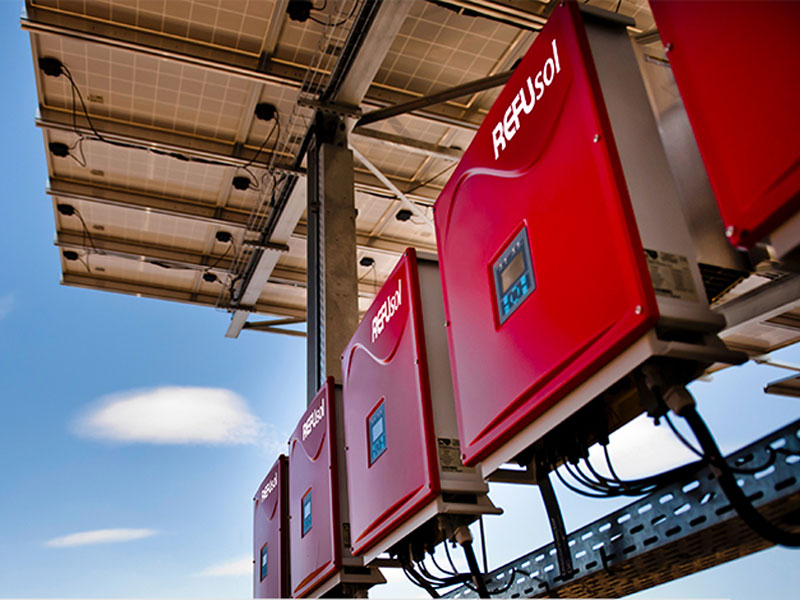
Solar inverter:
- Solar inverter is likened to the heart of the system, determines the stable operation of the system and determines the quality of power produced, so this is the most important device of the system.
-
Intermediate and protection systems:
- This system consists of conductors and equipment for connection, switching, measurement and protection installed inside the electrical cabinet.
-
Two-way galvanometer:
Two-way galvanometer (Net-metering) is often supplied and installed by Electricity agencies to measure power in two directions, in the direction of electricity consumption and in the opposite direction, to generate electricity to the grid. The measurement of these two power flows serves as the basis for calculating electricity bills according to the “offsetting” mechanism.